XML的三种解析方式
在阅读MyBatis解析器模块中的XPathParser类时,需要了解一些关于XML文档解析的相关知识
XML常见的解析方式有三种 DOM解析 SAX解析 STAX解析
下面将详细记录SAX解析的过程和代码
DOM解析
DOM属于是前端选手的老朋友了,它会基于树的形式将整个xml文档读入内存维护,基于这棵树结构对各个节点(Node)进行操作。

如下经过DOM解析后的树结构:
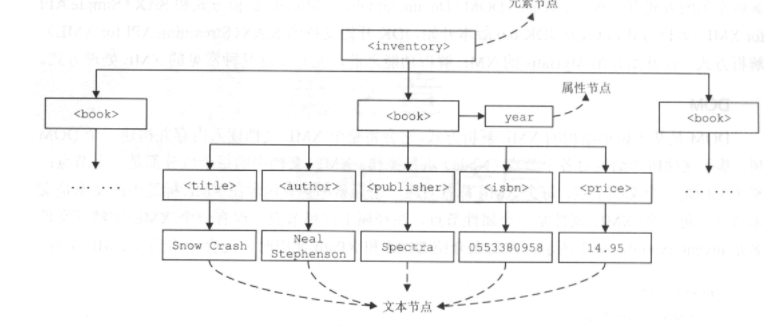
DOM解析的好处是因为基于树存储,易于节点之间的定位导航。但缺点也很明显,由于需要一次性读入到内存中,当文档过大时会造成较大的资源消耗
SAX解析
SAX解析在一定程度上解决了上面所述的资源消耗问题,它并不需要将整个文档加载到内存,只需将XML文档的一部分加载,即可开始解析,在处理过程中不会在内存中缓存XML的数据,占用资源较小。当程序处理过程中满足条件时,也可以立即停止解析过程
当SAX解析器解析到某类型节点时,会call注册在该类型节点上的回调函数,一般情况下,开发人员只需继承DefaultHandler基类,重写对应事件的函数即可
比如以下xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<books>
<book id="1001">
<name>
神雕侠侣
</name>
<author>
金庸
</author>
</book>
</books>
|
当sax解析器开始运行的时候,会分别调用以下回调函数
startElement(books)
startElement(book)
startElement(name)
characters(神雕侠侣)
endElement(name)
startElement(author)
characters(金庸)
endElement(author)
endElement(book)
endElement(books)
例如我们需要将xml中的book转为实体类,只需要创建自己的处理类,继承DefaultHandler,重写对应的函数即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| public class CustomHandler extends DefaultHandler {
private Book bookCache;
private List<Book> books;
private String currentName;
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length) throws SAXException {
System.out.println("characters("+new String(ch,start,length)+")");
if(currentName.equalsIgnoreCase("author")){
this.bookCache.setAuthor(new String(ch,start,length));
}else if(currentName.equalsIgnoreCase("name")){
this.bookCache.setName(new String(ch,start,length));
}
}
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName, Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
System.out.println("startElement("+qName+")");
if(qName.equalsIgnoreCase("books")){
this.books = new ArrayList<>();
}else if(qName.equalsIgnoreCase("book")){
this.bookCache = new Book();
this.bookCache.setId(Long.parseLong(attributes.getValue("id")));
}
this.currentName = qName;
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName) throws SAXException {
System.out.println("endElement("+qName+")");
if(qName.equalsIgnoreCase("book")){
this.books.add(bookCache);
}
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return books;
}
}
|
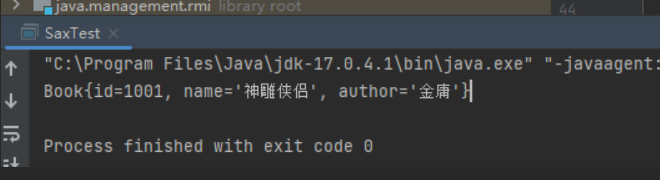
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class SaxTest {
private static XMLReader xmlReader(){
SAXParserFactory saxParserFactory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
SAXParser saxParser = null;
try {
saxParser = saxParserFactory.newSAXParser();
return saxParser.getXMLReader();
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SAXException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
XMLReader xmlReader = xmlReader();
CustomHandler customHandler = new CustomHandler();
xmlReader.setContentHandler(customHandler);
try {
xmlReader.parse(new InputSource(new FileInputStream(new File("bookdata.xml"))));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SAXException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
customHandler.getBooks().forEach(book -> System.out.println(book));
}
}
|
 ![])
![])
stax笔者未去了解过,感兴趣的可以参阅相关资料


